|
Quick links |
|
Exams Links |
|
|
Embedded Systems - Model-Based Design
Amazing ball (PID control)
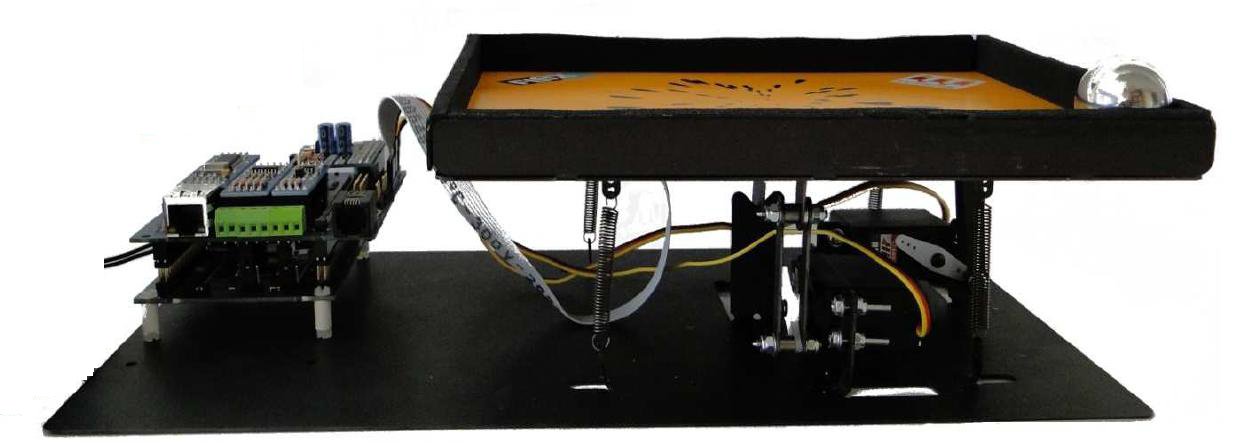
The device is shown in the picture.

Plant model
On the roll and pitch axis, the geometry of the assembly motor-plate is shown in figure
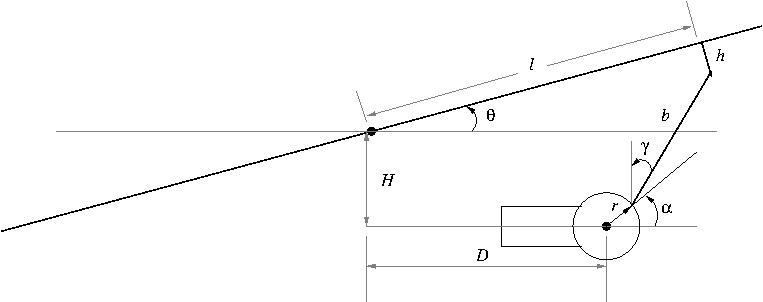
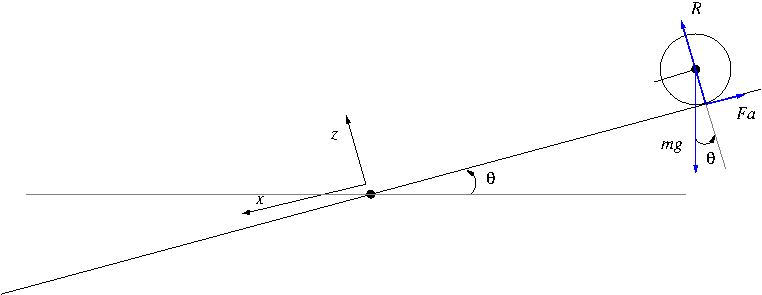
Document with the description of the assembly and the ball dynamics
Controller model
The Flex motion board is used to sense the position of the ball using the x,y input from the touchscreen (connected to two ADC channels on the board) and to control the position of the motors on the two axis, using the board PWM outputs.
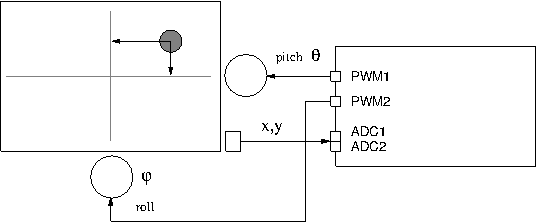
Simulink model
The Simulink model that is provided as part of the examples is shown in the following picture. It includes a model of the ball-and plate dynamics for the two axis, a 3D renderer of the ball and plate, a 2D scope showing the ball position on the plate and the PID controller.